Contents
- 1 Basic dialog
- 2 Grammar notes
- 3 Drills
- 3.1 Response drill
- 3.2 Chart I
- 3.3 Response drill
- 3.4 Chart II
- 3.5 Sentence combination drill
- 3.6 Expansion drill
- 3.7 Transformation drill
- 3.8 Substitution drill
- 3.9 Substitution drill
- 3.10 Combination drill
- 3.11 Combination drill
- 3.12 Combination drill
- 3.13 Combination drill
- 3.14 Recognition and Familiarization Drill
- 3.15 Substitution drill
- 4 Exercises
- 5 Vocabulary
Basic dialog
An appointment
| A. | มาหาใครครับ maa hǎa khray khráp |
Who did you come to see? |
| B. | คุณสวัสดิ์ อยู่ไหมครับ khun sawàt yùu mǎy khráp |
Is Mr. Sawat in? |
| A. | ไม่อยู่ครับ mây yùu khráp |
No, he isn't. |
| ออกไปข้างนอก ɔ̀ɔk pay khâaŋnɔ̂ɔk |
He went out. | |
| B. | จะกลับเมื่อไร ทราบไหมครับ cà klàp mʉ̂aray sâap mǎy khráp |
Do you know when he'll be back? |
| A. | เขาบอกว่าจะกลับก่อนเที่ยง kháw bɔ̀ɔk wâa cà klàp kɔ̀ɔn thîaŋ |
He said he'd be back before noon. |
| เชิญเข้ามานั่งคอยข้างในก่อนซิครับ chəən khâw maa nâŋ khɔɔy khâaŋnay kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp |
Please come in (and) sit down and wait. | |
| B. | ขอบคุณครับ khɔ̀ɔpkhun khráp |
Thank you. |
| (คุณบี เข้ามาในห้องรับแขก) ( khun bee khâw maa nay hɔ̂ŋrápkhɛ̀ɛk ) |
(Mr. B comes into the reception room): |
| B. | อ้อขอโทษ ที่นี่มีโทรศัพท์ไหมครับ ɔ̂ɔ khɔ̌ɔthôot thîinîi mii thoorasàp mǎy khráp |
Excuse me, is there a telephone here? |
| A. | มีครับ mii khráp |
Yes, there is. |
| B. | (ผม)ใช้(โทรศัพท์)หน่อย ได้ไหมครับ (phǒm) cháy (thoorasàp) nɔ̀y dâay mǎy khráp |
May I use it? |
| A. | เชิญครับ chəən khráp |
Go ahead. |
| อยู่บนโต๊ะตัวนั้น yùu bon tó tua nán |
It's on that desk. | |
| เห็นไหมครับ hěn mǎy khráp |
Do you see it? | |
| B. | เห็นแล้วครับ ขอบคุณมาก hěn lɛ́ɛw khráp khɔ̀ɔpkhun mâak |
I see it. Thanks very much. |
Notes on the dialog
- มาหา /maa hǎa/ means come to see someone.
- Both ทราบ /sâap/ and รู้ /rúu/ mean to know a fact, ทราบ /sâap/ is more formal than รู้ /rúu/ . In many constructions they are interchangeable, but not in all. In the following examples only รู้ /rúu/ may be used.
| เขารู้หนังสือ kháw rúu naŋsʉ̌ʉ |
He is literate. |
| เขารู้ภาษาอังกฤษ kháw rúu phaasǎa aŋkrìt |
He knows English. |
| ภาษาไทยของเขาแย่มาก phaasǎa thay khɔ̌ɔŋ kháw yɛ̂ɛ mâak |
His Thai is very bad. |
| ผมฟังไม่รู้เรื่อง phǒm faŋ mây rúu rʉ̂aŋ |
I don't understand what he's saying. |
- รู้จัก /rúucàk/ means to be acquainted with a person or thing.
Grammar notes
Sentence embedding
One sentence (called a 'constituent sentence') may be embedded in another sentence (called a 'matrix sentence'). The embedded sentence stands in a particular relationship to the matrix sentence; for example, it may serve as object complement of the main verb, or in some other relationship. The examples below illustrate this.
อยู่ + Location with Motion Verbs
| A: | เขา kháw |
นั่ง nâŋ |
He is sitting. | |
| B: | เขา kháw |
อยู่ข้างหน้า yùu khâaŋnâa |
He is in front. | |
| A/B: | เขา kháw |
นั่ง nâŋ |
อยู่ข้างหน้า yùu khâaŋnâa |
He is sitting in front. |
The sentence อยู่ /yùu/ + Location is embedded in the sentence เขานั่ง /kháw nâŋ/ and indicates the location of the action. It has the same function when it occurs with other verbs of motion like ยืน /yʉʉn/ , ไป /pay/ , etc.
Included sentence as object complement of main verb
ADD TABLE HERE:
| A: | คุณทราบ khun sâap |
... | You know. | |
| B: | เขาอยู่ที่ไหน kháw yùu thîinǎy |
Where does he live? | ||
| A/B: | คุณทราบ khun sâap |
ว่า wâa |
เขาอยู่ที่ไหน kháw yùu thîinǎy |
You know where he lives. |
Certain verbs like ทราบ /sâap/ 'to know a fact', พูด /phûut/ 'to speak', etc., normally have sentences as object complements. ว่า /wâa/ serves as an obligatory connector when the verb precedes its object.
ขอ as request form
| A: | ผม phǒm |
ขอ khɔ̌ɔ |
I request... | ||
| B: | ผม phǒm |
ใช้โทรศัพท์ cháy thoorasàp |
I use the telephone. |
| A/B: l. | ผม phǒm |
ขอ khɔ̌ɔ |
ใช้โทรศัพท์ cháy thoorasàp |
I request (to be allowed) to use the telephone. | |
| A/B: 2. | ขอ khɔ̌ɔ |
ผม phǒm |
ใช้โทรศัพท์ cháy thoorasàp |
I request (to be allowed) to use the telephone. | |
| A/B: 3. | ขอ khɔ̌ɔ |
ใช้โทรศัพท์ cháy thoorasàp |
I request (to be allowed) to use the telephone. |
Either l, 2, or 3 may be used. 3 is probably more common than l or 2. There is no difference in meaning in the three. The subject pronoun may be omitted only when it is ผม /phǒm/ or ดิฉัน /dìchǎn/ . This request form is often followed by ได้ไหมครับ /dâay mǎy khráp/ as in ขอใช้โทรศัพท์(หน่อย) ได้ไหมครับ /khɔ̌ɔ cháy thoorasàp ( nɔ̀y ) dâay mǎy khráp/ , to which the response is ได้ครับ /dâay khráp/ 'go ahead'.
Drills
Response drill
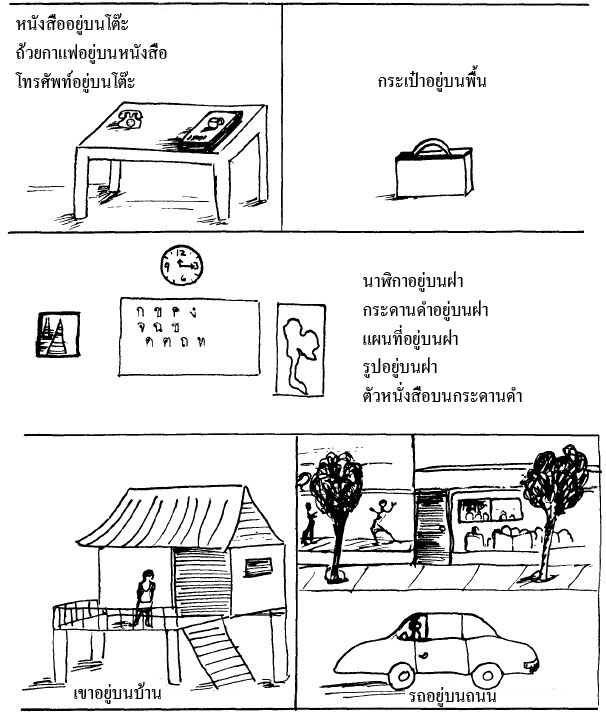
Use Chart I (below)
| Question | Answer | |
| 1. | โทรศัพท์อยู่ที่ไหน thoorasàp yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนโต๊ะ yùu bon tó |
| Where is the telephone? | On the table. | |
| 2. | ถ้วยกาแฟอยู่ที่ไหน thûay kaafɛɛ yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนหนังสือ (โต๊ะ) yùu bon naŋsʉ̌ʉ ( tó ) |
| Where is the coffee cup? | On the book, (table) | |
| 3. | กระเป๋าอยู่ที่ไหน kràpǎw yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนพื้น yùu bon phʉ́ʉn |
| Where is the suitcase? | On the floor. | |
| 4. | แผนที่อยู่ที่ไหน phɛ̌ɛn thîiyùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนฝา yùu bon fǎa |
| Where is the map? | On the wall. | |
| 5. | เขาอยู่ที่ไหน kháw yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนบ้าน yùu bon bâan |
| Where is he? | In the house. | |
| 6. | รถอยู่ที่ไหน rót yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนถนน yùu bon thanǒn |
| Where is the car? | On the street. |
Chart I
Response drill
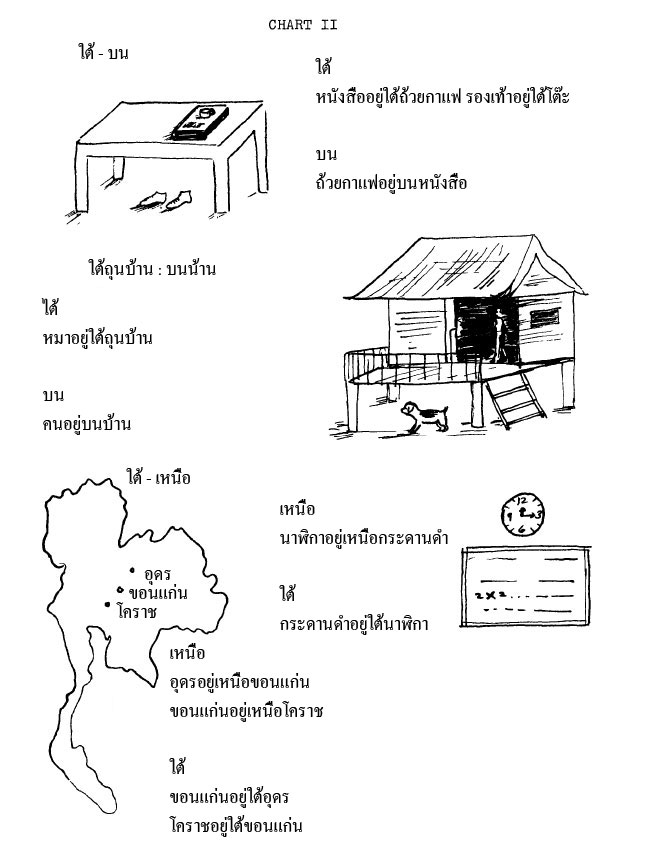
Use Chart II (below)
| Question | Answer | |
| 1. | รองเท้าอยู่ที่ไหน rɔɔŋtháaw yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่ใต้โต๊ะ yùu tây tó |
| Where are the shoes? | Under the table. | |
| 2. | หนังสืออยู่ที่ไหน naŋsʉ̌ʉ yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนโต๊ะ ใต้ถ้วยกาแฟ yùu bon tó tây thûay kaafɛɛ |
| Where is the book? | On the table...under the coffee cup. | |
| 3. | คนอยู่ที่ไหน khon yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่บนบ้าน yùu bon bâan |
| Where is the person? | In the house. | |
| 4. | หมาอยู่ที่ไหน mǎa yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่ใต้ถุนบ้าน yùu tây thǔn bâan |
| Where is the dog? | In the space under the house. | |
| 5. | จังหวัดอุดรอยู่ที่ไหน caŋwàt ùdɔɔn yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่เหนือขอนแก่น yùu nʉ̌a khɔ̌ɔnkɛ̀n |
| Where is Udorn Province? | It is north of Konkaen. | |
| 6. | จังหวัดขอนแก่นอยู่ที่ไหน caŋwàt khɔ̌ɔnkɛ̀n yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่เหนือโคราช/ใต้อุดร yùu nʉ̌a khoorâat/tâay ùdɔɔn |
| Where is Konkaen Province? | It is north of Korat/south of Udorn. | |
| 7. | นาฬิกาอยู่ที่ไหน naalíkaa yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่เหนือกระดานดำ yùu nʉ̌a kràdaandam |
| Where is the clock? | It is above the blackboard. | |
| 8. | กระดานดำอยู่ที่ไหน kràdaandam yùu thîinǎy |
อยู่ใต้นาฬิกา yùu tây naalíkaa |
| Where is the blackboard? | It is below the clock. |
Chart II
Sentence combination drill
| Pattern 1 and 2 | Pattern 3 | |
| 1. | เขานั่ง kháw nâŋ |
เขานั่งอยู่ข้างหน้า kháw nâŋ yùu khâaŋnâa |
| เขาอยู่ข้างหน้า kháw yùu khâaŋnâa |
He is sitting in front. | |
| 2. | เขายืน kháw yʉʉn |
เขายืนอยู่ข้างๆ ประตู kháw yʉʉn yùu khâaŋkhâaŋ pràtuu |
| เขาอยู่ข้างๆ ประตู kháw yùu khâaŋkhâaŋ pràtuu |
He is standing beside the door. | |
| 3. | เขานอน kháw nɔɔn |
เขานอนอยู่บนเตียง kháw nɔɔn yùu bon tiaŋ |
| เขาอยู่บนเตียง kháw yùu bon tiaŋ |
He is sleeping on (in) the bed. | |
| 4. | เขานั่ง kháw nâŋ |
เขานั่งอยู่ในรถ kháw nâŋ yùu nay rót |
| เขาอยู่ในรถ kháw yùu nay rót |
He is sitting in the car. | |
| 5. | เขายืน kháw yʉʉn |
เขายืนอยู่ที่สี่แยก kháw yʉʉn yùu thîi sìiyɛ̂ɛk |
| เขาอยู่ที่สี่แยก kháw yùu thîi sìiyɛ̂ɛk |
He is standing on the corner. | |
| 6. | เขานั่ง kháw nâŋ |
เขานั่งอยู่ที่เก้าอี้ kháw nâŋ yùu thîi kâwîi |
| เขาอยู่ที่เก้าอี้ kháw yùu thîi kâwîi |
He is sitting in the chair. | |
| 7. | เขานั่ง kháw nâŋ |
เขานั่งอยู่ทางขวา kháw nâŋ yùu thaaŋkhwǎa |
| เขาอยู่ทางขวา kháw yùu thaaŋkhwǎa |
He is sitting on the right. | |
| 8. | เขายืน kháw yʉʉn |
เขายืนอยู่ทางซ้ายผม kháw yʉʉn yùu thaaŋsáay phǒm |
| เขาอยู่ทางซ้ายผม kháw yùu thaaŋsáay phǒm |
He is standing to the left of me. | |
| 9. | เขานั่ง kháw nâŋ |
เขานั่งอยู่บนบ้าน kháw nâŋ yùu bon bâan |
| เขาอยู่บนบ้าน kháw yùu bon bâan |
He is sitting in the house. |
Expansion drill
| 1. | นั่ง nâŋ |
| นั่งซิครับ nâŋ sí khráp | |
| นั่งก่อนซิครับ nâŋ kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญนั่งก่อนซิครับ chəən nâŋ kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญนั่งที่นี่ก่อนซิครับ chəən nâŋ thîinîi kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญนั่งคอยที่นี่ก่อนซิครับ chəən nâŋ khɔɔy thîinîi kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| 2. | เข้ามา khâwmaa |
| เข้ามาซิครับ khâwmaa sí khráp | |
| เข้ามาก่อนซิครับ khâwmaa kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญเข้ามาก่อนซิครับ chəən khâwmaa kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญเข้ามาข้างในก่อนซิครับ chəən khâwmaa khâaŋnay kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญเข้ามานั่งข้างในก่อนซิครับ chəən khâwmaa nâŋ khâaŋnay kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp | |
| เชิญเข้ามานั่งคอยข้างในก่อนซิครับ chəən khâwmaa nâŋ khɔɔy khâaŋnay kɔ̀ɔn sí khráp |
Transformation drill
| Pattern 1 | Pattern 2 | |
| 1. | (เขา)จะกลับเมื่อไหร่ (kháw) cà klàp mʉ̂arày |
คุณทราบไหมครับ ว่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa |
| (คุณ)ทราบไหมครับ (khun) sâap mǎy khráp |
เขาจะกลับเมื่อไหร่ kháw cà klàp mʉ̂arày | |
| Do you know when he will return? | ||
| 2. | (เขา)ไปเมื่อไหร่ (kháw) pay mʉ̂arày |
คุณทราบไหมครับ ว่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa |
| (คุณ)ทราบไหมครับ (khun) sâap mǎy khráp |
เขาไปเมื่อไหร่ kháw pay mʉ̂arày | |
| Do you know when he went? | ||
| 3. | (เขา)ทำงานที่ไหน (kháw) thamŋaan thîinǎy |
คุณทราบไหมครับ ว่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa |
| (คุณ)ทราบไหมครับ (khun) sâap mǎy khráp |
เขาทำงานที่ไหน kháw thamŋaan thîinǎy | |
| Do you know where he works? | ||
| 4. | (เขา)ชื่ออะไร (kháw) chʉ̂ʉ àray |
คุณทราบไหมครับ ว่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa |
| (คุณ)ทราบไหมครับ (khun) sâap mǎy khráp |
เขาชื่ออะไร kháw chʉ̂ʉ àray | |
| Do you know what his name is? | ||
| 5. | สถานทูตอังกฤษอยู่ที่ไหน sathǎanthûut aŋkrìt yùu thîinǎy |
คุณทราบไหมครับ ว่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa |
| (คุณ)ทราบไหมครับ (khun) sâap mǎy khráp |
สถานทูตอังกฤษอยู่ที่ไหน sathǎanthûut aŋkrìt yùu thîinǎy | |
| Do you know where the British Embassy is? | ||
| 6. | เขาเป็นใคร kháw pen khray |
คุณทราบไหมครับ khun sâap mǎy khráp |
| คุณทราบไหมครับ khun sâap mǎy khráp |
ว่าเขาเป็นใคร wâa kháw pen khray | |
| Do you know who (what) he is? | ||
| 7. | เขาจะไปกี่วัน kháw cà pay kìi wan |
คุณทราบไหมครับ khun sâap mǎy khráp |
| คุณทราบไหมครับ khun sâap mǎy khráp |
ว่าเขาจะไปกี่วัน wâa kháw cà pay kìi wan | |
| Do you know how many days he'll be gone? | ||
| 8. | ที่สถานทูตมีคนเท่าไหร่ thîi sathǎanthûut mii khon thâwrày |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่า ที่ khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa thîi |
| คุณทราบไหมครับ khun sâap mǎy khráp |
สถานทูตมีคนเท่าไหร่ sathǎanthûut mii khon thâwrày | |
| Do you know how many people are at the embassy? |
Substitution drill
| Cue | Pattern | |
| 1. | เรื่อง rʉ̂aŋ |
เขารู้เรื่อง kháw rúu rʉ̂aŋ |
| He understands. | ||
| 2. | เรื่องนี้ rʉ̂aŋ níi |
เขารู้เรื่องนี้ kháw rúu rʉ̂aŋ níi |
| He understands this matter. | ||
| 3. | เรื่องคนอเมริกัน rʉ̂aŋ khon ameeríkan |
เขารู้เรื่องคนอเมริกัน kháw rúu rʉ̂aŋ khon ameeríkan |
| He understands Americans. | ||
| 4. | เบอร์โทรศัพท์ผม bəə thoorasàp phǒm |
เขารู้เบอร์โทรศัพท์ผม kháw rúu bəə thoorasàp phǒm |
| He knows my telephone number. | ||
| 5. | ว่าคุณเป็นใคร wâa khun pen khray |
เขารู้ว่าคุณเป็นใคร kháw rúu wâa khun pen khray |
| He knows who you are. | ||
| 6. | ว่าผมไม่ชอบเขา wâa phǒm mây chɔ̂ɔp kháw |
เขารู้ว่าผมไม่ชอบเขา kháw rúu wâa phǒm mây chɔ̂ɔp kháw |
| He knows I don't like him. |
Substitution drill
| Cue | Pattern | |
| 1. | คุณ khun |
เขารู้จักคุณ kháw rúucàk khun |
| He knows you. | ||
| 2. | ผม phǒm |
เขารู้จักผม kháw rúucàk phǒm |
| He knows me. | ||
| 3. | ชื่อคุณ chʉ̂ʉ khun |
เขารู้จักชื่อคุณ kháw rúucàk chʉ̂ʉ khun |
| He knows your name. | ||
| 4. | สนามหลวง sanǎamlǔaŋ |
เขารู้จักสนามหลวง kháw rúucàk sanǎamlǔaŋ |
| He is acquainted with (knows where it is) the Pramane Grounds. | ||
| 5. | คำนี้ kham níi |
เขารู้จักคำนี้ kháw rúucàk kham níi |
| He is familiar with this word. | ||
| 6. | คนไทยหลายคน khon thay lǎay khon |
เขารู้จักคนไทยหลายคน kháw rúucàk khon thay lǎay khon |
| He knows many Thais. | ||
| 7. | ทางไปบ้านคุณ thaaŋ pay bâan khun |
เขารู้จักทางไปบ้านคุณ kháw rúucàk thaaŋ pay bâan khun |
| He knows the way to your house. |
Combination drill
| Pattern 1 and 2 | Pattern 3 | |
| 1. | ตลาดอยู่ที่ไหน talàat yùu thîinǎy |
ผมทราบว่าตลาดอยู่ที่ไหน phǒm sâap wâa talàat yùu thîinǎy |
| ผมทราบ phǒm sâap |
I know where the market is. | |
| 2. | เขาทำงานอะไร kháw thamŋaan àray |
ผมทราบว่าเขาทำงานอะไร phǒm sâap wâa kháw thamŋaan àray |
| ผมทราบ phǒm sâap |
I know where he works. | |
| 3. | เขาเป็นคนดี kháw pen khondii |
ผมทราบว่าเขาเป็นคนดี phǒm sâap wâa kháw pen khondii |
| ผมทราบ phǒm sâap |
I know he's a good person. | |
| 4. | แถวไหนมีร้านอาหาร thɛ̌ɛw nǎy mii ráanaahǎan |
เขาทราบว่าแถวไหนมีร้านอาหารดีๆ kháw sâap wâa thɛ̌ɛw nǎy mii ráanaahǎan dii dii |
| เขาทราบ kháw sâap |
He knows in which section there are good restaurants. | |
| 5. | คุณเก่ง khun kèŋ |
เขาทราบว่าคุณเก่ง kháw sâap wâa khun kèŋ |
| เขาทราบ kháw sâap |
He knows you are skillful. |
Combination drill
| Pattern 1 and 2 | Pattern 3 | |
| 1. | นั่น, ใคร nân, khray |
คุณทราบไหมว่านั่นใคร khun sâap mǎy wâa nân khray |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know who that over there is? | |
| 2. | เขาชอบอะไร kháw chɔ̂ɔp àray |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าเขาชอบอะไร khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa kháw chɔ̂ɔp àray |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know what he likes? | |
| 3. | ห้องสมุดอยู่ที่ไหน hɔ̂ŋsamùt yùu thîinǎy |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าห้องสมุดอยู่ที่ไหน khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa hɔ̂ŋsamùt yùu thîinǎy |
| คุณทราบไหมครับ khun sâap mǎy khráp |
Do you know where the library is? | |
| 4. | เขามาเมื่อไหร่ kháw maa mʉ̂arày |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าเขามาเมื่อไหร่ khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa kháw maa mʉ̂arày |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know when he came? | |
| 5. | พรุ่งนี้เขาจะมาไหม phrûŋníi kháw cà maa mǎy |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าพรุ่งนี้เขาจะมาไหม khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa phrûŋníi kháw cà maa mǎy |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know if he is coming tomorrow? | |
| 6. | เมื่อวานนี้เขาไปทำงานหรือเปล่า mʉ̂awaan níi kháw pay thamŋaan rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
คุณทราบไหมว่าเมื่อวานนี้เขาไปทำงานหรือเปล่า khun sâap mǎy wâa mʉ̂awaan níi kháw pay thamŋaan rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know whether he went to work yesterday or not? | |
| 7. | เขาพูดภาษาไทยได้หรือเปล่า kháw phûut phaasǎa thay dâay rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าเขาพูดภาษาไทยได้หรือเปล่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa kháw phûut phaasǎa thay dâay rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know if he speaks Thai or not? | |
| 8. | เขาพิมพ์ดีดได้ดีหรือเปล่า kháw phimdìit dâay dii rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าเขาพิมพ์ดีดได้ดีหรือเปล่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa kháw phimdìit dâay dii rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know whether he can type well? | |
| 9. | เขาชอบทานอาหารฝรั่งหรือเปล่า kháw chɔ̂ɔp thaan aahǎan faràŋ rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
คุณทราบไหมครับว่าเขาชอบทานอาหารฝรั่งหรือเปล่า khun sâap mǎy khráp wâa kháw chɔ̂ɔp thaan aahǎan faràŋ rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
| คุณทราบไหม khun sâap mǎy |
Do you know if he likes foreign food? |
Combination drill
| Pattern 1 and 2 | Pattern 3 | |
| 1. | เขานั่งอยู่ที่ไหน kháw nâŋ yùu thîinǎy |
ผมไม่ทราบว่าเขา phǒm mây sâap wâa kháw |
| ผมไม่ทราบ phǒm mây sâap |
นั่งอยู่ที่ไหน nâŋ yùu thîinǎy | |
| I don't know where she is sitting. | ||
| 2. | คุณไม่ชอบเขา khun mây chɔ̂ɔp kháw |
ผมไม่ทราบว่าคุณ phǒm mây sâap wâa khun |
| ผมไม่ทราบ phǒm mây sâap |
ไม่ชอบเขา mây chɔ̂ɔp kháw | |
| I didn't know that you didn't like her. | ||
| 3. | เขายังเป็นโสด kháw yaŋ pensòot |
ผมไม่ทราบว่าเขา phǒm mây sâap wâa kháw |
| ผมไม่ทราบ phǒm mây sâap |
ยังเป็นโสด yaŋ pensòot | |
| I didn't know that he was still single. | ||
| 4. | เขาแต่งงานแล้วหรือยัง kháw tɛ̀ŋŋaan lɛ́ɛw rʉ̌ʉyaŋ |
ผมไม่ทราบว่าเขา phǒm mây sâap wâa kháw |
| ผมไม่ทราบ phǒm mây sâap |
แต่งงานแล้วหรือยัง tɛ̀ŋŋaan lɛ́ɛw rʉ̌ʉyaŋ | |
| I didn't know whether he was married or not. | ||
| 5. | เขาจะมาไหม kháw cà maa mǎy |
ผมไม่ทราบว่าเขาจะ phǒm mây sâap wâa kháw cà |
| ผมไม่ทราบ phǒm mây sâap |
มาไหม maa mǎy | |
| I don't know if she will come or not. |
Combination drill
| Pattern 1 and 2 | Pattern 3 | |
| 1. | เขาทำได้หรือเปล่า kháw tham dâay rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
ผมไม่ได้ถามว่า phǒm mây dây thǎam wâa |
| ผมไม่ได้ถาม(เขา) phǒm mây dây thǎam (kháw) |
เขาทำได้หรือเปล่า kháw tham dâay rʉ̌ʉplàaw | |
| I didn't ask if he could do it. | ||
| 2. | เขาจะกลับมาไหม kháw cà klàp maa mǎy |
ผมไม่ได้ถามว่า phǒm mây dây thǎam wâa |
| ผมไม่ได้ถาม phǒm mây dây thǎam |
เขาจะกลับมาไหม kháw cà klàp maa mǎy | |
| I didn't ask if he would return. | ||
| 3. | เขาเคยทำงานอะไร kháw khəəy thamŋaan àray |
ผมไม่ได้ถามว่า phǒm mây dây thǎam wâa |
| ผมไม่ได้ถาม(เขา) phǒm mây dây thǎam (kháw) |
เขาเคยทำงานอะไร kháw khəəy thamŋaan àray | |
| I didn't ask what he used to do. | ||
| 4. | เขาเป็นคนดีไหม kháw pen khon dii mǎy |
คุณถามเพื่อนคุณ khun thǎam phʉ̂an khun |
| คุณถามเพื่อนคุณหรือเปล่า khun thǎam phʉ̂an khun rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
หรือเปล่าว่าเขาเป็นคนดีไหม rʉ̌ʉplàaw wâa kháw pen khon dii mǎy | |
| Did you ask your friend if he is a good person? | ||
| 5. | เขาอยู่ที่ไหน kháw yùu thîinǎy |
คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
| คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
ว่าเขาอยู่ที่ไหน wâa kháw yùu thîinǎy | |
| Did you ask him where he lived? | ||
| 6. | เขาเข้าใจไหม kháw khâwcay mǎy |
คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
| คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
ว่าเขาเข้าใจไหม wâa kháw khâwcay mǎy | |
| Did you ask him if he understood? | ||
| 7. | คุณสมศักดิ์อยู่หรือไม่อยู่ khun sǒmsàk yùu rʉ̌ʉ mây yùu |
คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่าว่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw wâa |
| คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
คุณสมศักดิ์อยู่หรือไม่อยู่ khun sǒm sàk yùu rʉ̌ʉ mây yùu | |
| Did you ask him if Somsak was in or not? | ||
| 8. | เขาจะมาได้ไหม kháw cà maa dâay mǎy |
คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่าว่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw wâa |
| คุณถามเขาหรือเปล่า khun thǎam kháw rʉ̌ʉplàaw |
เขาจะมาได้ไหม kháw cà maa dâay mǎy | |
| Did you ask him if he would be able to come? |
Recognition and Familiarization Drill
| 1. | ขอใช้โทรศัพท์หน่อยได้ไหมครับ khɔ̌ɔ cháy thoorasàp nɔ̀y dâay mǎy khráp |
May I use the telephone? |
| 2. | ขอถามอะไรหน่อยได้ไหมครับ khɔ̌ɔ thǎam àray nɔ̀y dâay mǎy khráp |
May I ask something? |
| 3. | ขอดูหน่อยได้ไหมครับ khɔ̀ɔ duu nɔ̀y dâay mǎy khráp |
May I look? |
| 4. | ขอออกก่อนเวลาได้ไหมครับ khɔ̌ɔ ɔ̀ɔk kɔ̀ɔn weelaa dâay mǎy khráp |
May I leave ahead of time? |
| 5. | ขอออกก่อนเวลาสักสิบห้านาทีได้ไหมครับ khɔ̌ɔ ɔ̀ɔk kɔ̀ɔn weelaa sàk sìp hâa naathii dâay mǎy khráp |
May I leave 15 minutes ahead of time? |
Repeat the drill above two times. Use ผมขอ /phǒm khɔ̌ɔ/ one time and ขอผม /khɔ̌ɔ phǒm/ one time.
Substitution drill
| Cue | Pattern | |
| 1. | บอก bɔ̀ɔk |
เขาบอกว่าจะกลับก่อนเที่ยง kháw bɔ̀ɔk wâa cà klàp kɔ̀ɔnthîaŋ |
| He said he would return before noon. | ||
| 2. | คิด khít |
เขาคิดว่าจะกลับก่อนเที่ยง kháw khít wâa cà klàp kɔ̀ɔnthîaŋ |
| He thought he would return before noon. | ||
| 3. | พูด phûut |
เขาพูดว่าจะกลับก่อนเที่ยง kháw phûut wâa cà klàp kɔ̀ɔnthîaŋ |
| He said he would return before noon. | ||
| 4. | สั่ง sàŋ |
เขาสั่งว่าจะกลับก่อนเที่ยง kháw sàŋ wâa cà klàp kɔ̀ɔnthîaŋ |
| He left a message that he would return before noon. | ||
| 5. | โทรมาบอก thoo maa bɔ̀ɔk |
เขาโทรมาบอกว่าเขาจะกลับก่อนเที่ยง kháw thoo maa bɔ̀ɔk wâa kháw cà klàp kɔ̀ɔnthîaŋ |
| He called and said he would return before noon. |
Exercises
- One student asks another where various classroom objects are; another responds that they are on, above, under, etc. other objects.
- Using the map following page 74 (or a classroom map) discuss the relative positions ('north of, 'south of) of various Thai cities and provinces.
- Different students assume different positions in the classroom (standing by the door, sitting on the table, etc.). Other students describe the positions they are in.
- Have the students find out information about each other (where they live, whether they play tennis, if they are cold, etc.). Use conversational exchanges like the one below:
| Student A: | Do you know where Mr. C lives? |
| Student B: | No, I don't. |
| (to Student D): | Where does Mr. C live? |
| Student D: | I think he lives on Birch Street. |
| Student C: | No, I don't. I live on Elm Street. |
| (Student A to Student B): | Did you ask Mr. C where he lives? |
| Student B: | No, I didn't. I asked Mr. D. |
| Student A: | What did Mr. D say? |
| Student B: | He said he didn't know. |
| Student A: | Then you didn't ask Mr. C? |
| Student B: | No, I didn't. |
| Student A: | Ask him now. |
| (Student B to Student C): | Where do you live? |
| Student C: | On Elm Street. |
| Student B: | He said he lived on Elm Street. |
| Student A: | Thanks very much. |
- Student A asks Student B if he is familiar with a certain person or place. Student B responds that he is not familiar with the person or place and asks for further information (where a thing is or who a person is). Student A provides the information.
- Student A asks the instructor for permission to perform some act (close the window, open his book, etc.) The instructor responds to the request either negatively or affirmatively.
- One student asks another his opinion about something. The second student gives an opinion.
Vocabulary
| อ๋อ ɔ̌ɔ |
oh |
| เบอร์ (เบอร์) bəə ( bəə ) |
number (classifier for rooms, telephone, clothing size, etc.) |
| เชิญ chəən |
please |
| ชอบ chɔ̂ɔp |
to like |
| ฝา (ฝา) fǎa ( fǎa ) |
wall |
| เห็น hěn |
to see |
| ห้องรับแขก (ห้อง) hɔ̂ŋrápkhɛ̀ɛk ( hɔ̂ŋ ) |
reception room, living room |
| ยืน yʉʉn |
to stand |
| คำ kham |
word |
| คิด khít |
to think |
| คน khon |
person (classifier for person) |
| ขอ khɔ̌ɔ |
to request, ask |
| คอย khɔɔy |
to wait |
| กระเป๋า (ใบ) kràpǎw ( bay ) |
suitcase, bag, purse |
| หมา mǎa |
dog |
| นั่ง nâŋ |
to sit |
| นอน nɔɔn |
to sleep |
| พิมพ์ดีด phimdìit |
to type, print |
| พื้น phʉ́ʉn |
floor |
| รองเท้า (คู่) rɔɔŋtháaw ( khûu ) |
shoes (pair) |
| รู้เรื่อง rúurʉ̂aŋ |
to understand |
| เรื่อง (เรื่อง) rʉ̂aŋ |
story (about), about / (classifier for story) |
| สัก sàk |
a little, bit |
| สนามหลวง sanǎamlǔaŋ |
the Pramane Grounds |
| สั่ง sàŋ |
to order, to leave instructions or a message |
| สวัสดิ์ sawàt |
Sawat (name) |
| ซี, ซิ sii, sí |
particle indicating definiteness or emphasis |
| ใต้ tây/tâay |
under |
| ใต้ถุน tâythǔn |
the space under the house |
| ถาม thǎam |
to ask,(a question) |
| ถ้วย (ใบ) thûay ( bay ) |
cup (classifier for a cup of something) |
| เตียง (เตียง) tiaŋ ( tiaŋ ) |
bed (to sleep on) |
| ตัวหนังสือ (ตัว) tuanaŋsʉ̌ʉ ( tua ) |
letter (of the alphabet) |
| วัน (วัน) wan ( wan ) |
day (classifier for day) |